Yubikey vs Onlykey Which One Is For You?
Yubikey and Onlykey provide better security features than 2-factor authentication. Let’s talk briefly about Yubikey vs Onlykey in this article. Being aware of your digital security is a crucial factor that leads to a safer online presence. Online security has always been a topic of discussion in the world of security and reliability. As we have discovered at this point in the digital era, passwords are not sufficient to keep your account and data safe. In fact, it is a weak way of protecting your information. With just a right guess, anyone can enter your account and get access to your sensitive information. Developers have produced an extra layer of security with the introduction of the 2FA Method and U2F.
Difference between Yubikey and OnlyKey
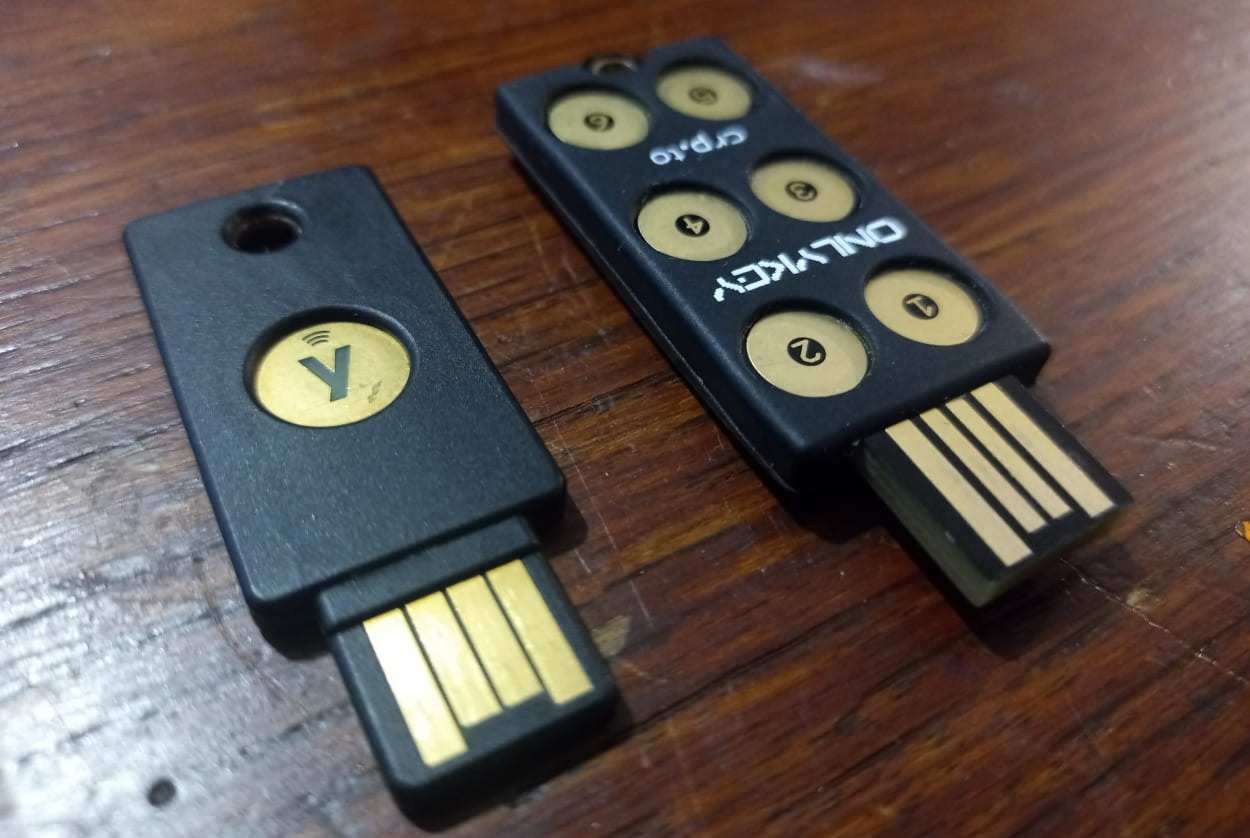 Hardware-based authentication methods such as YubiKey and OnlyKey solve the flaws in conventional password-based security. Even though they both aim to increase online security, they differ in certain ways that make them useful.
Hardware-based authentication methods such as YubiKey and OnlyKey solve the flaws in conventional password-based security. Even though they both aim to increase online security, they differ in certain ways that make them useful.
Authentication Methods
YubiKey: YubiKey’s FIDO-based authentication makes it compatible with a variety of systems and apps. Strong security for online accounts is provided by it when used with FIDO-compliant services.  OnlyKey: OnlyKey provides a variety of authentication choices. It can operate with websites that demand a password as long as it is 56 characters long and supports a wider range of protocols. OnlyKey may be used as a hardware token by itself or in conjunction with passwords.
OnlyKey: OnlyKey provides a variety of authentication choices. It can operate with websites that demand a password as long as it is 56 characters long and supports a wider range of protocols. OnlyKey may be used as a hardware token by itself or in conjunction with passwords.

Form Factors
YubiKey: To accommodate varied devices and user preferences, YubiKey provides a variety of form factors, including USB, NFC, and USB-C. This gives you versatility while using the gadget.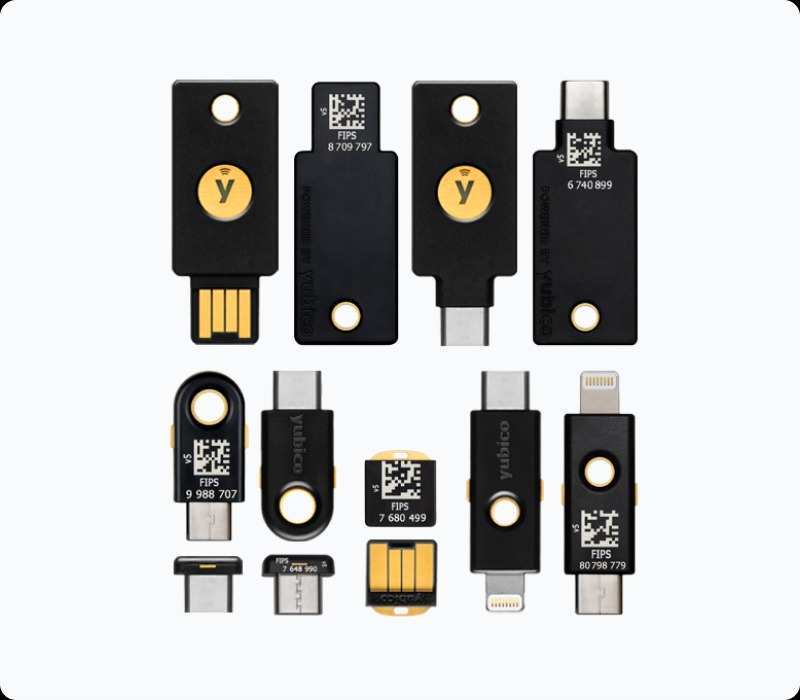  OnlyKey: NFC/Bluetooth/USB and USB/NFC are among the form factors available for OnlyKey. Moreoever, the FIDO standard of 2FA in Onlykey is powerful security feature.
OnlyKey: NFC/Bluetooth/USB and USB/NFC are among the form factors available for OnlyKey. Moreoever, the FIDO standard of 2FA in Onlykey is powerful security feature.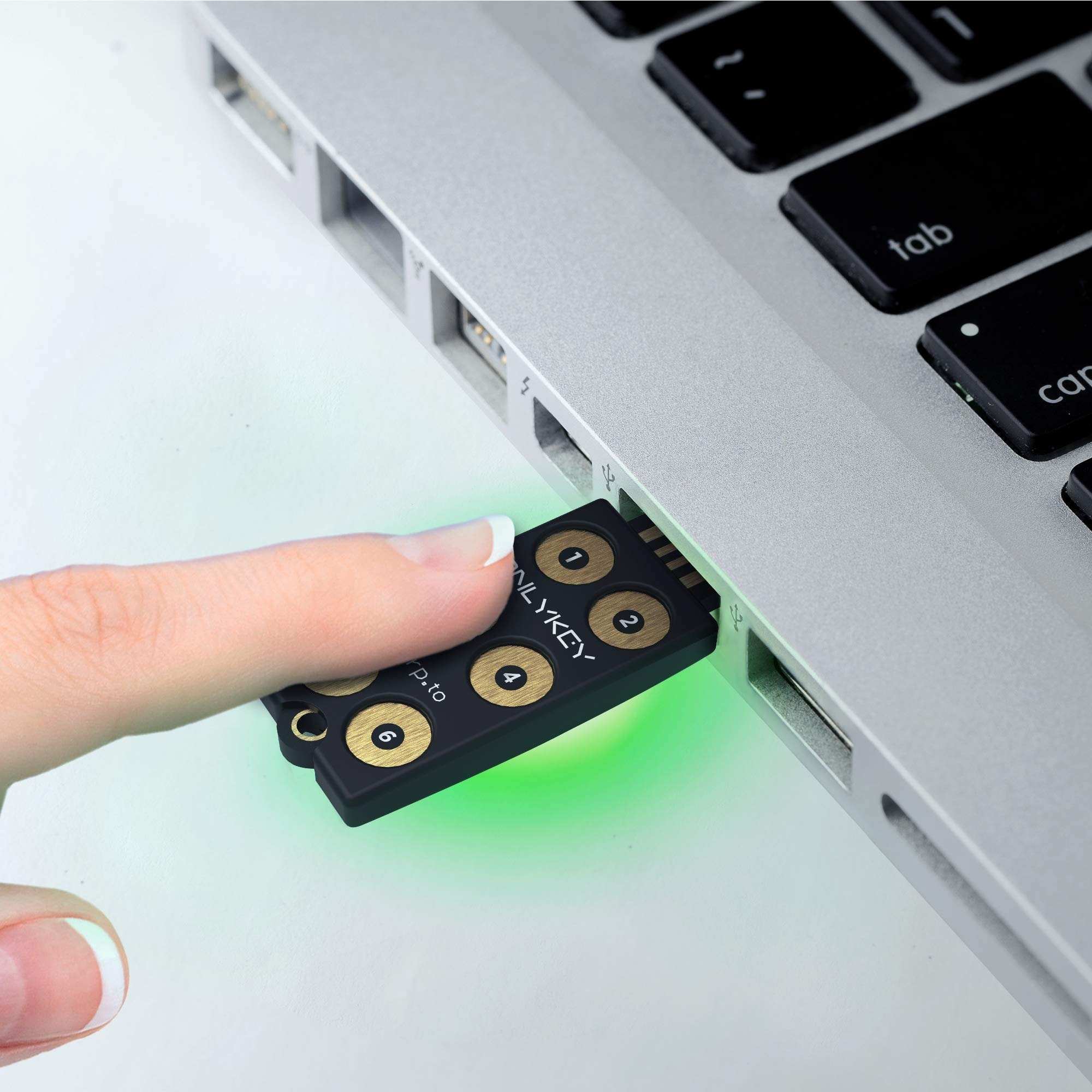 
Mobile Experience
YubiKey: YubiKey adds FIDO features to improve the mobile experience. Users may easily validate their identity on mobile devices thanks to this functionality.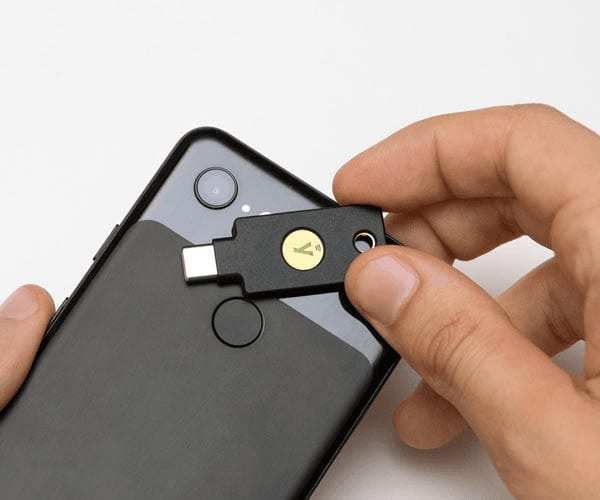  OnlyKey: OnlyKey caters to consumers who need mobility and flexibility. It has two form factors NFC, Bluetooth, and USB. As a result, there are many common ways you can access your data.
OnlyKey: OnlyKey caters to consumers who need mobility and flexibility. It has two form factors NFC, Bluetooth, and USB. As a result, there are many common ways you can access your data.
Compatibility
YubiKey: YubiKey’s FIDO-based authentication makes it compatible with a variety of systems and apps. Strong security for online accounts is provided by it when used with FIDO-compliant services.  OnlyKey: OnlyKey offers tap-and-go authentication that works flawlessly with Windows 10 devices and Android apps. It is also the only device that also has a two-factor authentication. The fact that OnlyKey may be used with any website as long as the password requirements are satisfied is a noteworthy benefit. It becomes a more flexible choice as a result, especially for customers with many online accounts..
OnlyKey: OnlyKey offers tap-and-go authentication that works flawlessly with Windows 10 devices and Android apps. It is also the only device that also has a two-factor authentication. The fact that OnlyKey may be used with any website as long as the password requirements are satisfied is a noteworthy benefit. It becomes a more flexible choice as a result, especially for customers with many online accounts..
Passwords
YubiKey: YubiKey, which mostly relies on FIDO standards, recommends eschewing conventional passwords. It emphasizes passwordless authentication, which is safer and less susceptible to hackers. OnlyKey: While encouraging the use of hardware-based authentication, OnlyKey permits users to utilize lengthy, complicated passwords as long as they are no longer than 56 characters. Users who believe they have a very strong sets of passwords will love this complicated password method. Moreover, it also has both U2F and 2FA security systems.
Conclusion
In Summary, by eliminating reliance on conventional passwords, YubiKey and OnlyKey are both good options for enhancing online security. YubiKey shines with its emphasis on FIDO standards and acceptance of passwordless authentication. It provides a flexible range of form factors and a potent secondary or primary element of authentication. However, OnlyKey offers more platform compatibility and supports both password-based and passwordless authentication. Moreover, it is extremely adaptable in terms of use cases, making it appropriate for a variety of online scenarios. The decision between YubiKey and OnlyKey ultimately comes down to personal preferences and the user’s particular security needs.